NEWS
- 24
-
2025
12
Quality Control in PCBA Manufacturing: Processes, Pain Points, and Practical QC Know-How
Quality Control in PCBA Manufacturing: Beyond Inspection
In PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) manufacturing, quality control is often perceived as a final safeguard, an inspection step meant to catch visible defects before shipment. However, in practice,
PCBA quality failures rarely originate at the inspection stage. They are usually the result of upstream decisions: component sourcing, PCB fabrication quality, process parameters, or incomplete design-for-manufacturing (DFM) alignment.
As PCB designs become more compact, multilayered, and component-dense, QC in PCBA manufacturing has evolved from a simple defect-detection function into a systematic risk-control mechanism. Effective QC today requires coordination across procurement, engineering, production, and inspection teams.
This article explores PCBA-specific QC from end to end:
-
How QC works across the PCBA process
-
Where quality pain points commonly arise
-
Key inspection techniques used in PCBA
-
The difference between QC “know-what” and “know-how”
-
Critical discussion points for teams selecting or evaluating a PCBA partner
Why QC Is Especially Critical in PCBA
Unlike mechanical products, PCBA failures are often:
-
Invisible (micro-cracks, voids, marginal solder joints)
-
Intermittent (thermal or vibration-induced failures)
-
System-wide (one PCB failure can bring down an entire device)
Once a PCBA enters final product assembly, rework becomes expensive or impossible. This makes quality control in PCBA manufacturing less forgiving and far more dependent on process discipline rather than post-assembly correction.
The PCBA Quality Control Framework
1. Incoming Quality Control (IQC) in PCBA
Objective:
Ensure all incoming materials meet assembly and reliability requirements before entering the SMT or THT process.
IQC scope in PCBA typically includes:
-
Electronic components (ICs, passives, connectors)
-
Bare PCBs
-
Solder paste and flux
-
Packaging materials and trays
Common PCBA-specific IQC checks:
-
Component packaging condition (MSL, moisture barrier bags)
-
Date codes and lot traceability
-
PCB surface finish quality (ENIG, OSP, HASL)
-
Solderability and oxidation
-
Dimensional accuracy and warpage
Key PCBA pain point:
Component shortages often force substitutions. Without strong IQC controls,
electrically equivalent parts may behave differently during reflow, leading to latent defects.
2. In-Process Quality Control (IPQC) in PCBA
Objective:
Monitor and stabilize the assembly process to prevent defect accumulation.
Critical IPQC checkpoints:
-
Solder paste printing
-
SMT placement accuracy
-
Reflow temperature profiling
-
Through-hole soldering
-
Manual assembly steps
Typical IPQC inspection items:
-
Solder paste volume and alignment
-
Component skew, tombstoning, or misplacement
-
Solder joint wetting and fillet shape
-
Reflow profile consistency
Key PCBA pain point:
IPQC effectiveness often depends on operator experience rather than quantified limits, making results inconsistent across shifts or lines.
3. Outgoing Quality Control (OQC) in PCBA

Objective:
Confirm assembled boards meet functional, cosmetic, and documentation requirements before shipment.
OQC activities in PCBA include:
-
Final visual inspection
-
AOI verification
-
Functional or in-circuit testing
-
Labeling and traceability checks
-
Packaging and ESD protection verification
Key PCBA pain point:
OQC is often expected to compensate for upstream weaknesses—an unrealistic role that increases scrap and rework cost.
Common PCBA Quality Pain Points Across the Industry
1. Same BOM, Different Assembly Outcomes
Even with identical BOMs, PCBA quality can vary due to:
-
Component sourcing channels
-
PCB fabrication tolerances
-
Assembly process windows
-
Operator handling
QC systems must account for variation, not just compliance.
2. Design and Manufacturing Misalignment
Many PCBA defects originate from:
-
Insufficient DFM review
-
Overly tight pad designs
-
Inadequate solder mask openings
-
Inconsistent stack-up tolerances
QC cannot fix a design that is inherently unstable in production.
3. Over-Dependence on Visual Inspection
Visual inspection remains essential but:
-
Cannot detect internal voids
-
Misses micro-fractures
-
Is highly subjective
In complex PCBA, visual checks alone provide false confidence.
4. Incomplete Feedback Loops
QC findings are often logged but not:
-
Trended
-
Reviewed cross-functionally
-
Used to adjust upstream parameters
This limits continuous improvement.
Key QC Techniques Used in PCBA Manufacturing
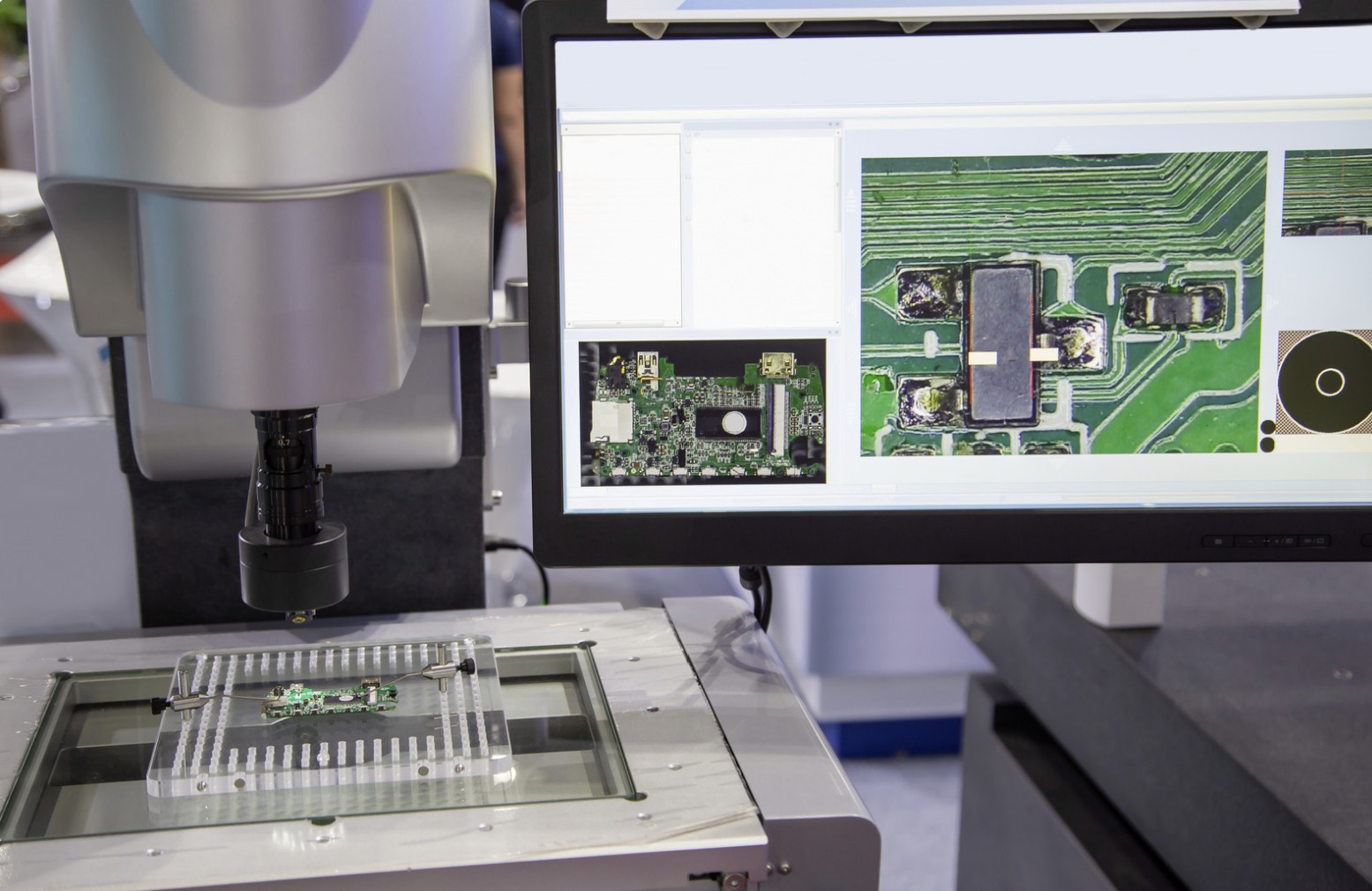

Automated Optical Inspection (AOI)
-
Detects placement and solder issues
-
High speed and repeatability
-
Limited context for functional impact
Best used as a process monitor, not a final authority.
X-Ray Inspection
-
Essential for BGA, QFN, and hidden joints
-
Identifies voids, bridges, and insufficient solder
-
Requires trained interpretation
Typically reserved for high-risk assemblies.
Functional Testing
-
Confirms real-world electrical performance
-
Highly application-specific
-
Requires test fixtures and upfront planning
Critical for reliability-sensitive products.
In-Circuit Testing (ICT)
-
Verifies individual component behavior
-
Requires stable test points
-
Less flexible for rapid design changes
Often paired with functional testing.
Sampling and AQL in PCBA
-
Controls inspection workload
-
Does not guarantee zero defects
-
Must align with product criticality
Misuse of AQL is a common QC mistake.
QC Know-What vs QC Know-How in PCBA
QC Know-What
-
IPC standards
-
Inspection stages
-
Defect classification
-
Acceptance criteria
Most PCBA suppliers possess this knowledge.
QC Know-How
-
Adjusting inspection depth by product risk
-
Identifying systemic vs isolated defects
-
Managing borderline solder conditions
-
Communicating risk transparently to customers
This distinguishes mature PCBA partners from commodity assemblers.
What to Look for When Evaluating PCBA QC Capability
Instead of asking only about certifications, consider asking:
-
Where do most of your PCBA defects originate—and how do you reduce them?
-
How do you handle component substitutions from a QC perspective?
-
How are reflow profiles validated and controlled?
-
How do QC findings feed back into process improvement?
-
How do you balance delivery pressure with quality risk?
The answers reveal real capability far better than inspection counts.
Discussion Points for Internal Teams
-
Are we inspecting to protect the customer or to protect the schedule?
-
Do our QC controls match the functional risk of the product?
-
Are we relying more on people or on controlled processes?
-
Is QC empowered to stop production when needed?
These questions help shift QC from a cost center to a strategic function.
Final Thoughts: QC as a Competitive Advantage in PCBA
In PCBA manufacturing, quality control is not a single checkpoint—it is an integrated system spanning design alignment, material control, process stability, and informed judgment.
Organizations that treat QC as:
-
A preventive tool rather than a corrective one
-
A shared responsibility across teams
-
A source of insight rather than blame
are better equipped to manage complexity, reduce long-term cost, and build lasting trust with customers.
In PCBA, quality is not inspected in, it is engineered, monitored, and reinforced at every stage.